
Try a Free Week!
Find your flow with a week of free unlimited yoga.
Core Class Types
Yoga Sculpt
Cardio + Weights
Yoga, cardio and strength moves boost metabolism and build lean muscle.
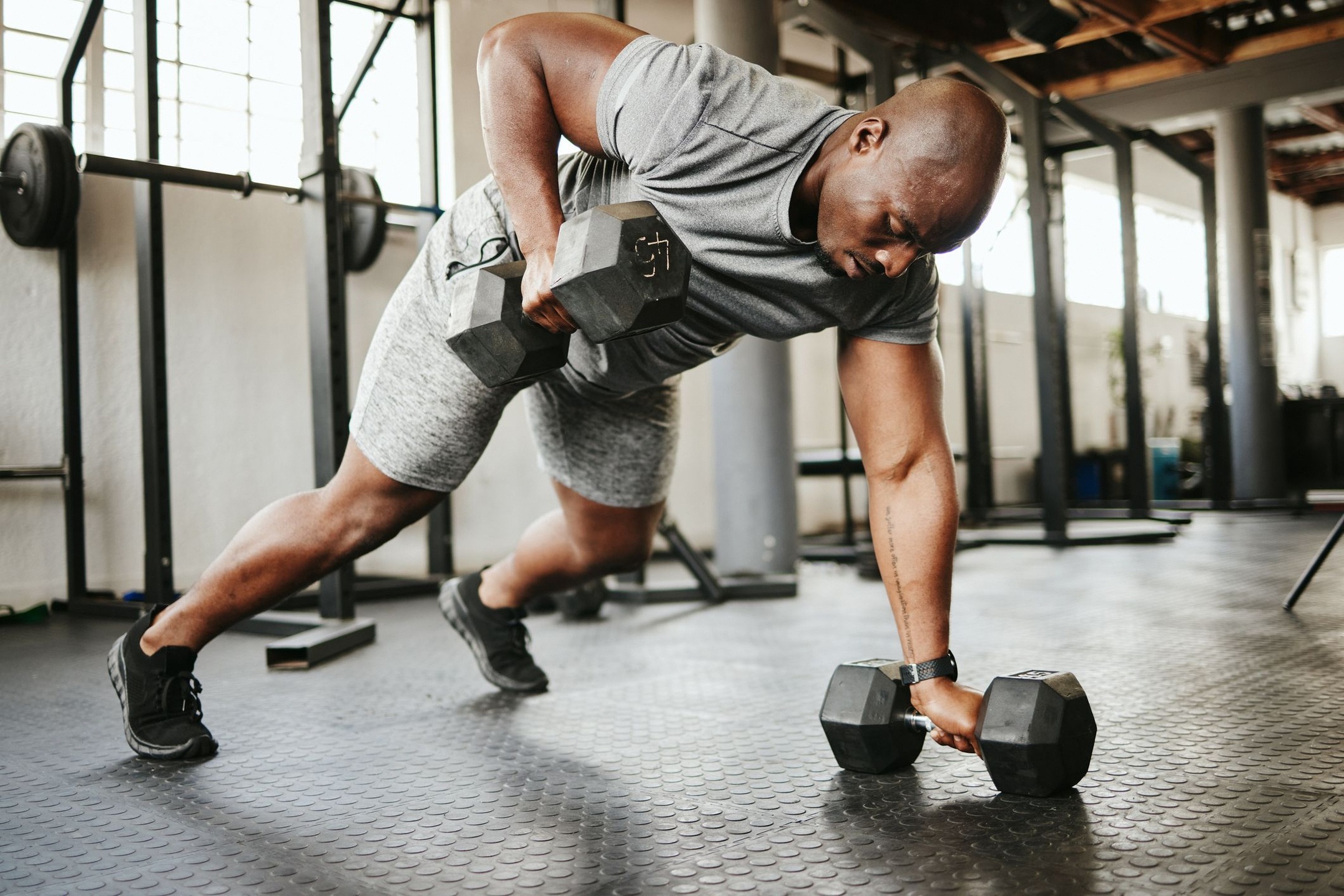

CorePower Strength X
Strength Training
Power your potential in this heart-pumping, strength training workout with energizing breathwork.
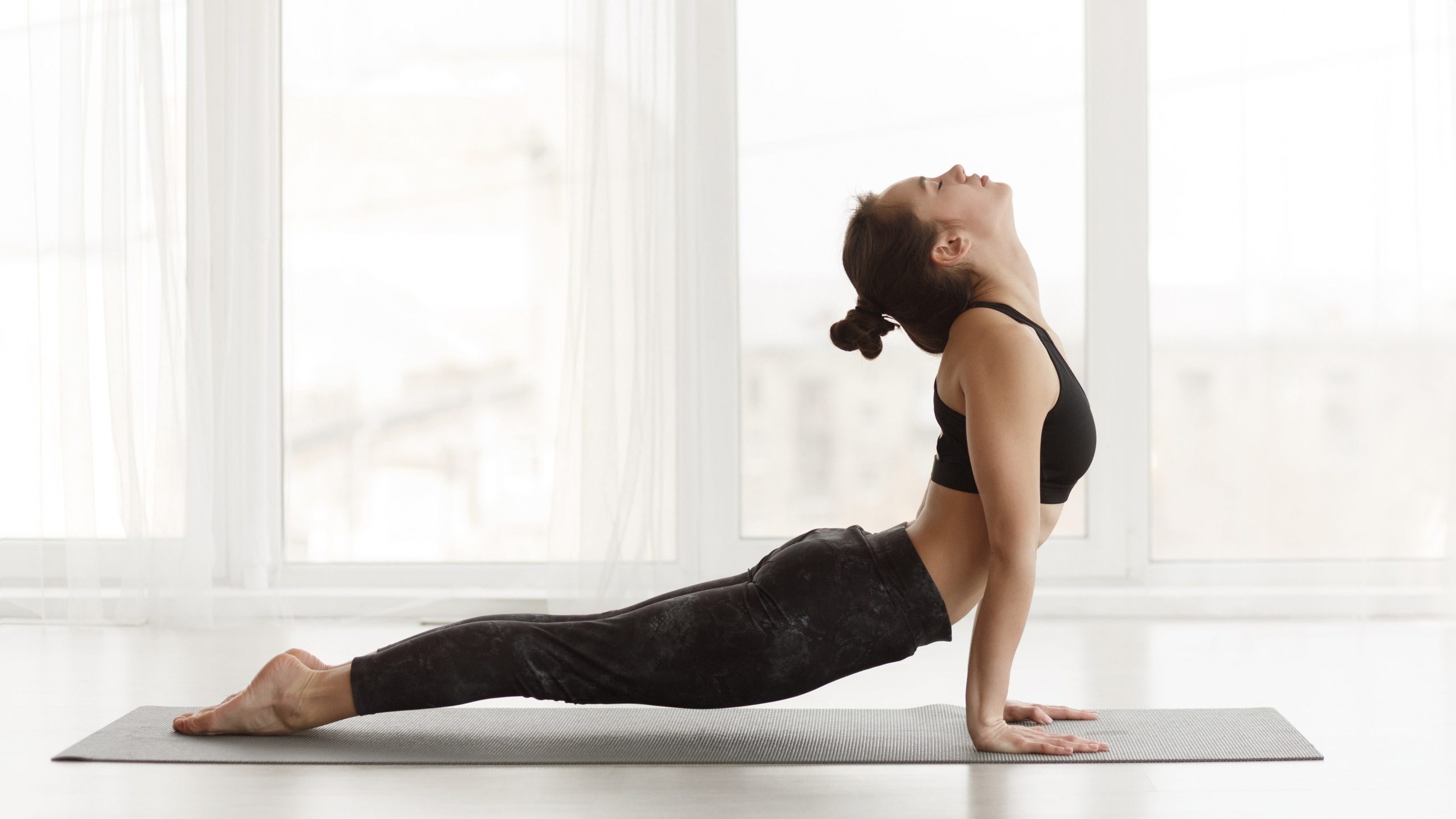

CorePower 1
Fundamental Flow
Explore the fundamental principles and postures of Vinyasa yoga with no added heat.
Find the right Membership For You
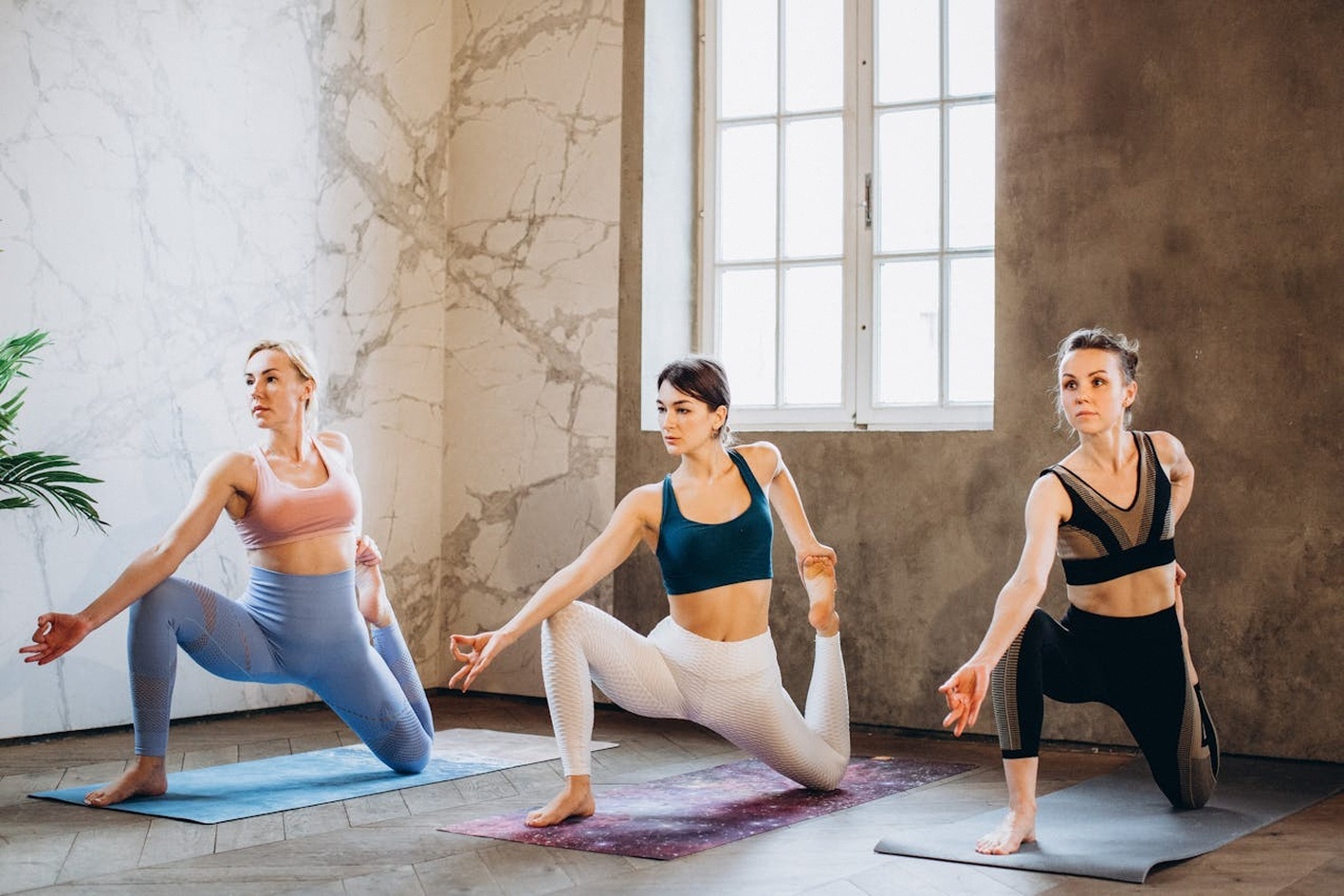

All Access Membership
Unroll your mat everywhere with unlimited access to studio, outdoor, livestream and on-demand classes (surcharges may apply in New York).

Studio Class Packs
Get access to our studio classes anytime with a variety of flexible class packs available for purchase—no membership required!

At Home Membership
Whether you're at home or on the go, our digital membership gets you access to unlimited livestream and on-demand classes.
We believe yoga can power transformation—on and off the mat
View Our Platforms

Join Us in Studio
We're open and ready for you! Find a studio near you to start flowing.
Stream Live on Zoom
Connect with teachers and students across the U.S. in 100+ real-time classes per week.

Take Class On Demand
Choose from our ever-growing library of classes for everyone, at every level.
Glowing Reviews
Our students share why they love CorePower Yoga!
"It is really empowering to see how your body can do so much. Being able to see that growth from class to class and just the changes in your own body and your strength, and your willpower to push a little bit harder is awesome."
"My favorite class is CoreRestore. I like to say that sometimes the hardest part of our practice is just getting still, and I think that every single human being on this planet could benefit from just stopping, and breathing, listening not just to their body but to themselves."
"My CorePower routine is my superpower! My practice helps me be consistent with self-care and self-love. I find myself craving it and when I come out of a class I feel renewed — out of my head and into my soul!"
Book Your Class
Find and book yoga classes at our studios or online
Available Classes
Yoga Sculpt
Downtown Studio • Sarah Johnson
CorePower 1
Online • Mike Chen
CorePower Strength X
Uptown Studio • Lisa Rodriguez
Memberships & Packages
Choose the perfect plan for your yoga journey
All Access Membership
- Unlimited studio classes
- Unlimited online classes
- Guest passes included
- Retail discounts
- Priority booking
Studio Class Pack
- 10 class pack: $220
- 5 class pack: $125
- Single class: $25
- No expiration
- Transferable
At Home Membership
- Unlimited online classes
- Live stream classes
- On-demand library
- Mobile app access
- Cancel anytime
CorePower Shop
Yoga Mats
From $45
Apparel
From $35
Accessories
From $15
Learn Yoga
Discover the fundamentals and deepen your practice
Beginner's Guide
New to yoga? Start here with our comprehensive guide to yoga basics, poses, and breathing techniques.
- Basic poses and alignment
- Breathing techniques
- Yoga philosophy
- What to expect in class
Class Types Explained
Understand the different styles of yoga we offer and find the perfect class for your goals.
- Vinyasa Flow
- Hot Yoga
- Yoga Sculpt
- Restorative Yoga
Wellness Resources
Enhance your practice with our collection of wellness articles, videos, and meditation guides.
- Meditation guides
- Nutrition tips
- Injury prevention
- Mindfulness practices
Free Practice Videos
20-Minute Morning Flow
Start your day with energy
Beginner Yoga Basics
Learn fundamental poses
Evening Relaxation
Unwind and restore
Teacher Training
Transform your practice and inspire others
200-Hour Yoga Teacher Training
Join our comprehensive teacher training program and deepen your practice while learning to guide others on their yoga journey.
Program Overview
- 200-hour certification
- Yoga Alliance registered
- Weekend intensive format
- Experienced instructors
- Small class sizes
Curriculum
- Anatomy & physiology
- Yoga philosophy
- Teaching methodology
- Sequencing & alignment
- Business of yoga
Investment
- Early bird: $2,495
- Regular price: $2,795
- Payment plans available
- Includes all materials
- Lifetime support